DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol in Computer Networks
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol in Computer Networks is explained with the following timecodes:
0:00 – DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol – Computer Network
1:08 – Basics of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
3:53 – Working of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
8:57 – Practical Example of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
The following points are covered in this video:
0. Computer Network
1. Network Layer
2. DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
3. Basics of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
4. Working of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
5. Practical Example of DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Engineering Funda channel is all about Engineering and Technology. Here this video is a part of Computer Network.
#DHCP #DynamicHostConfigurationProtocol #IPV4 #IPAddress #NetworkLayer #ComputerNetwork #EngineeringFunda
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used to automate the process of assigning IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network. It simplifies the administration of IP addresses by dynamically allocating them to devices as they connect to the network.
Here’s how DHCP works:
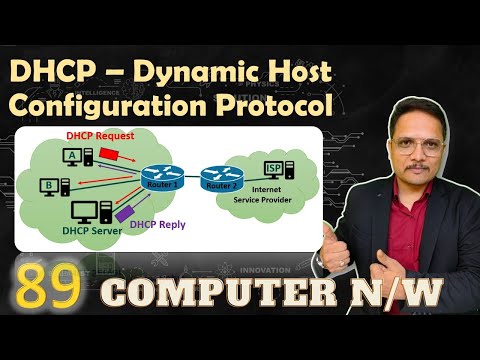
1. DHCP Discovery: When a device (referred to as a DHCP client) connects to a network, it broadcasts a DHCP discovery message to locate a DHCP server. The message is sent to the destination IP address 255.255.255.255 or the subnet’s broadcast address.
2. DHCP Offer: DHCP servers on the network receive the discovery message and respond with a DHCP offer message. The offer includes an available IP address, lease duration, and other configuration parameters such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses.
3. DHCP Request: The client receives multiple offers from different DHCP servers and selects one offer by sending a DHCP request message. The request confirms the chosen DHCP server and the offered configuration parameters.
4. DHCP Acknowledgment: The DHCP server that receives the request sends a DHCP acknowledgment message to the client, confirming the allocation of the requested IP address and providing the lease duration and other configuration details.
5. IP Address Lease: The client now has an IP address and can use it for communication on the network. The lease duration specifies the amount of time the client can use the IP address before it needs to renew the lease.
6. Lease Renewal: During the lease period, the client can choose to renew the lease by sending a DHCP request message to the DHCP server that initially assigned the IP address. The server may extend the lease or assign a new lease depending on the configuration.
DHCP simplifies network administration by automating the IP address assignment process, eliminating the need for manual configuration. It allows organizations to efficiently manage IP address allocation, handle device mobility, and facilitate easier network reconfiguration. DHCP also supports the allocation of additional network configuration parameters, such as subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server addresses, and more.
Overall, DHCP enables flexible and scalable management of IP addresses and network configurations, making it widely used in local area networks (LANs) and other network environments. .