How to configure DHCP on a cisco router in a VLAN environment, and enable interVLAN routing
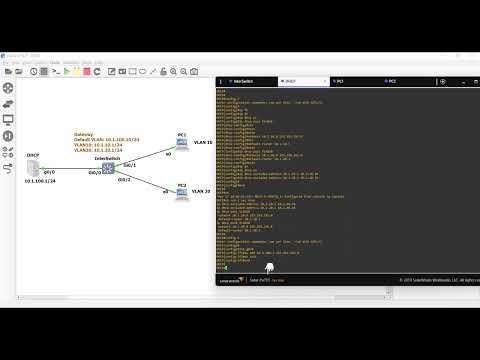
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on a Cisco router refers to the capability of the router to act as a DHCP server or DHCP relay agent. DHCP is a network protocol that automates the process of assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network.
When a Cisco router is configured as a DHCP server, it can dynamically allocate IP addresses to devices within its local network. The router maintains a pool of available IP addresses and leases them to devices when they connect to the network. The DHCP server also provides other network configuration information to the devices, such as DNS server addresses and domain names.
To configure a Cisco router as a DHCP server, you need to define a DHCP pool that specifies the range of IP addresses to be assigned, lease durations, and other configuration options. The router can then listen for DHCP requests from devices and respond with the appropriate IP address and configuration information.
On the other hand, a Cisco router can also function as a DHCP relay agent. In this role, the router forwards DHCP requests received from devices in one network to a DHCP server located in another network. This is useful in scenarios where the DHCP server is located on a different subnet or network segment. The relay agent adds its own IP address to the DHCP request as the source address and forwards it to the DHCP server, which then assigns an appropriate IP address and responds back to the relay agent. The relay agent then forwards the response back to the original requesting device. .